|
Year: 2012-
Member:
Yosuke Eguchi
Hideki Kadone
Kai Sasaki
Diego Felipe Paez Granados
Chen Yang
Yukiyo Shimizu
Kenji Suzuki
Partners:
- University Hospital, Rehabilitation Section
Tags:
- Cybernics
|
|
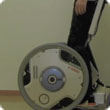
Qolo: A Standing Mobility Vehicle
A Standing Mobility Vehicle with Passive Exoskeleton Assisting Voluntary Postural Changes
|
|

|
|
This study proposes a novel personal mobility vehicle for supporting and assisting people with disabled lower limbs. The developed mobile platform is capable of assisting voluntary postural transition between standing and sitting, called the Passively Assistive Limb (PAL) mechanism, in addition to high mobility with upright posture. The device consists of gasspring-powered passive exoskeleton for postural support and two in-wheel motors for mobility support. The developed robot system allows a user to sit down on chairs and beds, and stand up through easy operations. In addition, a user can move the system in the standing posture without using their hands. In this paper, the development and assessments of the standing mobility vehicle are described.
This paper proposes a standing mobility vehicle consisting of a passive exoskeleton and electrically driven wheels. The exoskeleton is designed for maintaining the standing and sitting postures of the user, as well as assisting interpostural transitions and hands-free locomotion control. An assessment of the developed prototype verified advantage of the proposed approach. The developed PMV can maintain the user posture, as well as its motion can be controlled based on the attitude of the user’s trunk without the use of their upper limbs. One of the important situations in day-to-day PMV use is transferring a user from a bed to the PMV. The bed was configured at a height suitable for the PMV. The subject was then asked to perform the motion without using lower limb muscle as much as possible. The whole motion of transferring and wearing the PMV took about 100[s], and it was required for the user to handle their lower limbs using their upper limbs. Through this validation, it was confirmed that users can carry out the entire procedure on their own. The developed PMV is tailor-made for the subject. A mechanical adjustment system for other users of different sizes and body weights will be developed. Further investigation for ensuring PMV stability will be conducted in the future, as well as application to outdoor environments and other subjects.
|
|
This work is partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, MEXT, Japan.

This work is partly supported by FIRST Program: World leading Human-Assistive Technology.
|
| |
|
|
|
Publications
 Paez, D., Kadone, H., and Suzuki, K., "Unpowered Lower-Body Exoskeleton with Torso Lifting Mechanism for Supporting Sit-to-Stand Transitions," IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2018. (accepted) Paez, D., Kadone, H., and Suzuki, K., "Unpowered Lower-Body Exoskeleton with Torso Lifting Mechanism for Supporting Sit-to-Stand Transitions," IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2018. (accepted) Kai Sasaki, Paez, D., Sugimoto, M., Sugiyama, T., and Suzuki, K., "Child-sized Passive Exoskeleton for Supporting Voluntary Sitting and Standing Motions," IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2018. (accepted) Kai Sasaki, Paez, D., Sugimoto, M., Sugiyama, T., and Suzuki, K., "Child-sized Passive Exoskeleton for Supporting Voluntary Sitting and Standing Motions," IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2018. (accepted) Eguchi, Y., Kadone, H., and Suzuki, K., Standing Mobility Device with Passive Lower Limb Exoskeleton for Upright Locomotion, IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 23(4):1608-1618, 2018. Eguchi, Y., Kadone, H., and Suzuki, K., Standing Mobility Device with Passive Lower Limb Exoskeleton for Upright Locomotion, IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 23(4):1608-1618, 2018.- Eguchi, Y., Kadone, H., and Suzuki, K., "A Standing Mobility Vehicle with Passive Exoskeleton Assisting Voluntary Postural Changes," Proc. of 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2013), pp. 1190-1195, 2013.
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Related Projects
Cybernics / Augmented Human
|
|
|
|



